Leading the Industry in LNG-fueled Vessel Deployment Expanding Alternative Fuel Vessels Across Various Ship Types
Released : May 23, 2025
Updated : May 22, 2025
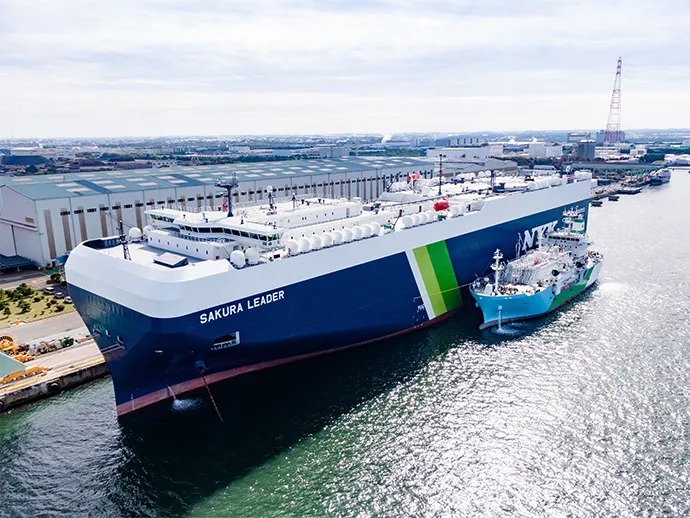

LNG bunkering operation by Kaguya for the PCTC Sakura Leader
The NYK Group has been leading the maritime industry in adopting low-carbon LNG-fueled vessels positioned to serve as a bridge solution until zero-emission fuels become a reality. The Group has achieved a world-first by constructing LNG-fueled car carriers and LNG bunkering vessels. In addition to its core strategy of transitioning from LNG to ammonia fuel, NYK is proactively introducing various alternative fuels such as LPG, methanol, and biofuels in collaboration with shippers and other stakeholders as a step tailored to match the needs of cargo for transport.
Expanding LNG-fueled Vessels and Bunkering Vessels
In 2015, NYK launched Japan’s first LNG-fueled vessel, the tugboat Sakigake, constructed by Keihin Dock Co., Ltd., and operated by Shin-Nippon Kaiyosha for towing services in the ports of Yokohama and Kawasaki. LNG bunkering (ship fueling) was carried out via the truck-to-ship method using flexible hoses.
Despite the large challenges faced in adopting LNG fuel for use in a tugboat having limited space for installing equipment and large fluctuations in engine output, the project was made feasible by utilizing technical expertise and technological capabilities cultivated by Keihin Dock over the years, dual-fuel LNG/heavy oil engines by Niigata Power Systems Co., Ltd. (now IHI Power Systems Co., Ltd.), and LNG supply systems developed by Air Water Plant & Engineering Inc. (now Air Water Engineering Inc.). After extensive sea trials and repeated verifications of operational aspects, the tugboat achieved excellent environmental performance and maintained the same hull form and maneuvering performance as conventional tugboats. This Sakigake project provided valuable knowledge and experience in the construction, operation, and bunkering of LNG-fueled vessels, not only for the NYK Group but also for Japan’s maritime industry.
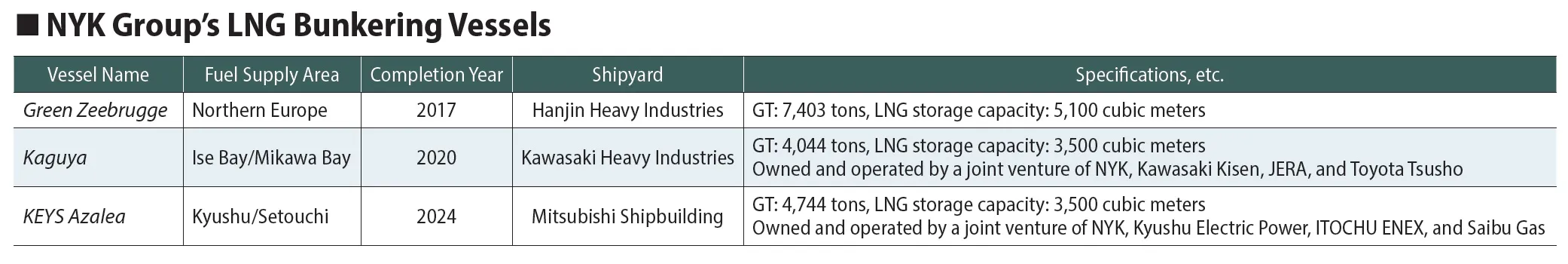
The adoption of LNG fuel for oceangoing vessels first progressed primarily in the car carrier sector, and the NYK Group was the first in the world to construct an LNG-fueled vessel in this field. NYK, in collaboration with Wallenius Lines, a Swedish owner of various maritime business entities, jointly invested in the European short-sea car carrier company United European Car Carriers (UECC). In 2016, UECC constructed two 4,000-vehicle capacity pure car and truck carriers (PCTCs) at Nantong COSCO KHI Ship Engineering Co., Ltd. (NACKS) in China. Since the operation of large LNG-fueled vessels requires ship-to-ship (STS) bunkering, NYK introduced the world’s first LNG bunkering vessel, Green Zeebrugge (formerly Engie Zeebrugge), in service in Europe to coincide with the deployment of LNG-fueled car carriers.
UECC currently operates five LNG-fueled PCTCs, the latest three equipped with battery hybrid propulsion systems to further enhance environmental performance. In 2024, UECC ordered two LNG-fueled battery hybrid PCTCs, thus expanding the use of liquefied biomethane (bio-LNG) fuel in its LNG-fueled car carriers.
In 2020, NYK commissioned Sakura Leader, a 7,000-vehicle capacity LNG-fueled PCTC built by Shin Kurushima Dockyard Co., Ltd., for deployment on long-distance ocean routes. NYK announced plans to construct 20 LNG-fueled car carriers, including this vessel, at domestic and overseas shipyards by 2028, thus creating a large transformative trend in fuel shift in the car carrier sector.
NYK, in collaboration with a joint venture involving Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha, Ltd. (“K” LINE), JERA Co., Inc., and Toyota Tsusho Corporation, placed into service Kaguya, Japan’s first LNG bunkering vessel for domestic operations. The vessel was built by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., to coincide with the launch of Sakura Leader. Based at JERA’s Kawagoe Thermal Power Station in Mie Prefecture, Kaguya carries out LNG bunkering operations in the Chubu region and recorded its 100th supply of LNG fuel in November 2024.
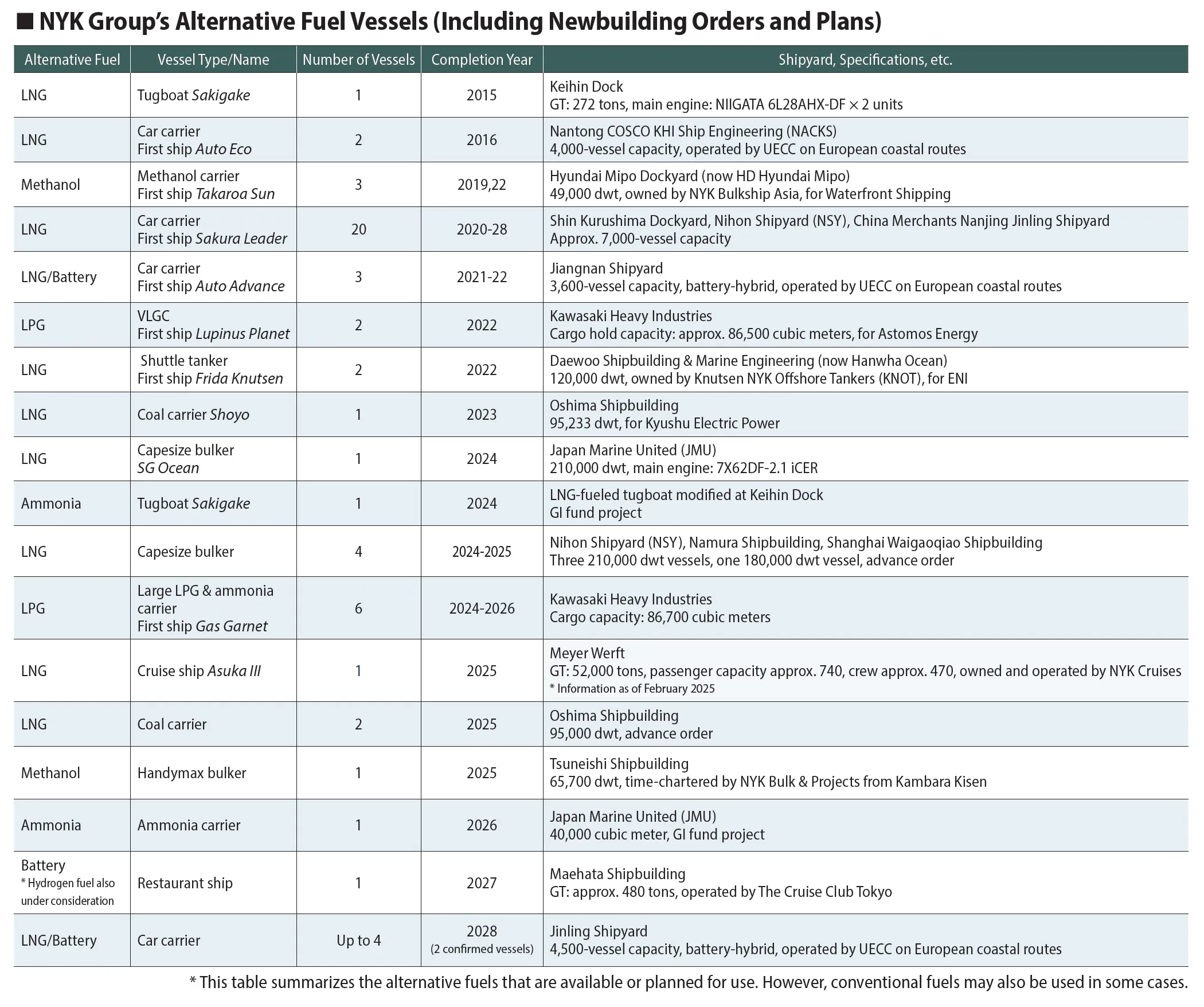
Advance Orders for LNG-fueled Vessels
NYK has also made further cutting-edge progress in the construction of LNG-fueled vessels in its dry bulk sector by building the world’s first LNG-fueled Panamax bulk carrier, the 95,233-dwt Shoyo, at Oshima Shipbuilding Co., Ltd. in 2023, and deployed it for transporting coal used in power generation by Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc. In another effort aligned with this, NYK, through its joint venture KEYS Bunkering West Japan with Kyushu Electric Power, ITOCHU ENEX CO., LTD., and Saibu Gas Co., Ltd., also made further progress in this field by constructing the LNG bunkering vessel KEYS Azalea, which was completed at the Shimonoseki Plant of Mitsubishi Shipbuilding Co., Ltd. in March 2024. The vessel has been conducting LNG bunkering operations in the Kyushu and Seto Inland Sea regions since April of the same year.
In 2024, Japan Marine United Corporation (JMU) constructed the 210,933-dwt LNG-fueled Capesize bulk carrier SG Ocean for JFE Steel Corporation. This marked the first time a domestic Japanese shipyard had built an LNG-fueled Capesize bulk carrier.
While NYK has been collaborating with shippers such as Kyushu Electric Power and JFE Steel to develop LNG-fueled vessels, the company also placed an advance order in 2022 for four LNG-fueled Capesize and two Panamax bulk carriers, despite not having already secured transport contracts with shippers at the time. Typically, Capesize and Panamax bulk carriers are only ordered after finalizing long-term contracts with shippers, especially since the higher costs of LNG-fueled vessels compared to conventional heavy-fuel oil-powered vessels must be considered. However, NYK took the bold step of preemptively ordering LNG-fueled vessels in this sector, thus demonstrating its strong commitment to leading the industry in developing eco-friendly vessels.
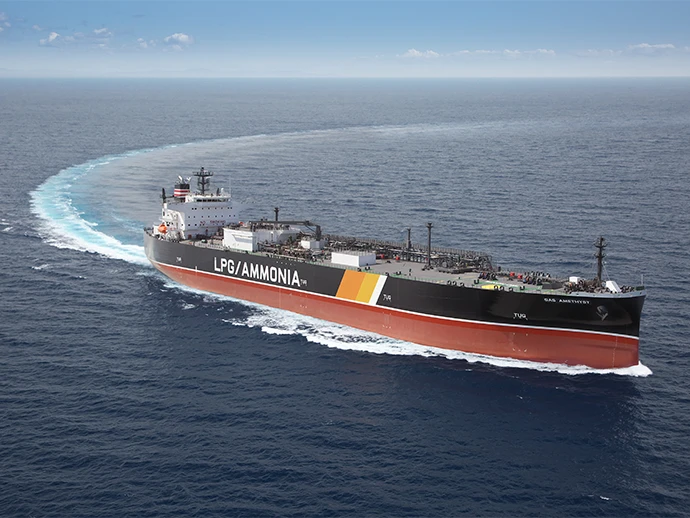

LPG-fueled LPG/ammonia carrier Gas Amethyst
Fuel Conversion Spanning Diverse Ship Types
Following its adoption of LNG-fueled vessels, NYK is actively introducing low-carbon alternative fuel LPG. In 2021, the company placed an order with Kawasaki Heavy Industries for its first two LPG-fueled huge gas carriers (VLGCs), with the first vessel delivered in September 2022 and the second in January 2023. Further, NYK has also ordered six LPG-fueled large LPG/ammonia carriers from Kawasaki Heavy Industries, with three of these vessels already delivered in 2024, one scheduled for delivery in 2025, and the remaining two scheduled for handover in 2026.
These LPG/ammonia carriers are equipped with dualfuel LPG engines as well as shaft generators. These shaft generators produce electricity during ocean voyages by utilizing the rotation of a shaft connected to the propeller from the main engine, allowing entire LPG-fueled operation except for minimal use of pilot fuel (a small amount of fuel injected before main fuel combustion to aid ignition). To prepare for future use of ammonia as fuel, these vessels have also been designed in conformance with Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK) issued guidelines.
NYK is promoting the adoption of alternative-fuel vessels not only in its own oceangoing cargo shipping business but also throughout its group companies, including cruise ships and shuttle tankers. Among these, NYK Bulk & Projects Carriers Ltd. (NBP) is working on the use of alternative fuels for handymax/handysize bulkers, which pose even more challenges due to their limited available space for fuel tanks and diverse port calls, making fuel conversion particularly difficult. To address these issues, NBP is moving ahead with GHG emission reduction measures by taking the dual approach of enhancing fuel efficiency via slow steaming and energy-saving technologies while also collaborating with shippers and shipyards to develop and construct next-generation fuel vessels. Currently, NBP is engaged in an ammonia-fueled Handymax bulk carrier construction project with overseas shippers and has also secured a new methanol-fueled Handymax charter contract from Kambara Kisen Co., Ltd.
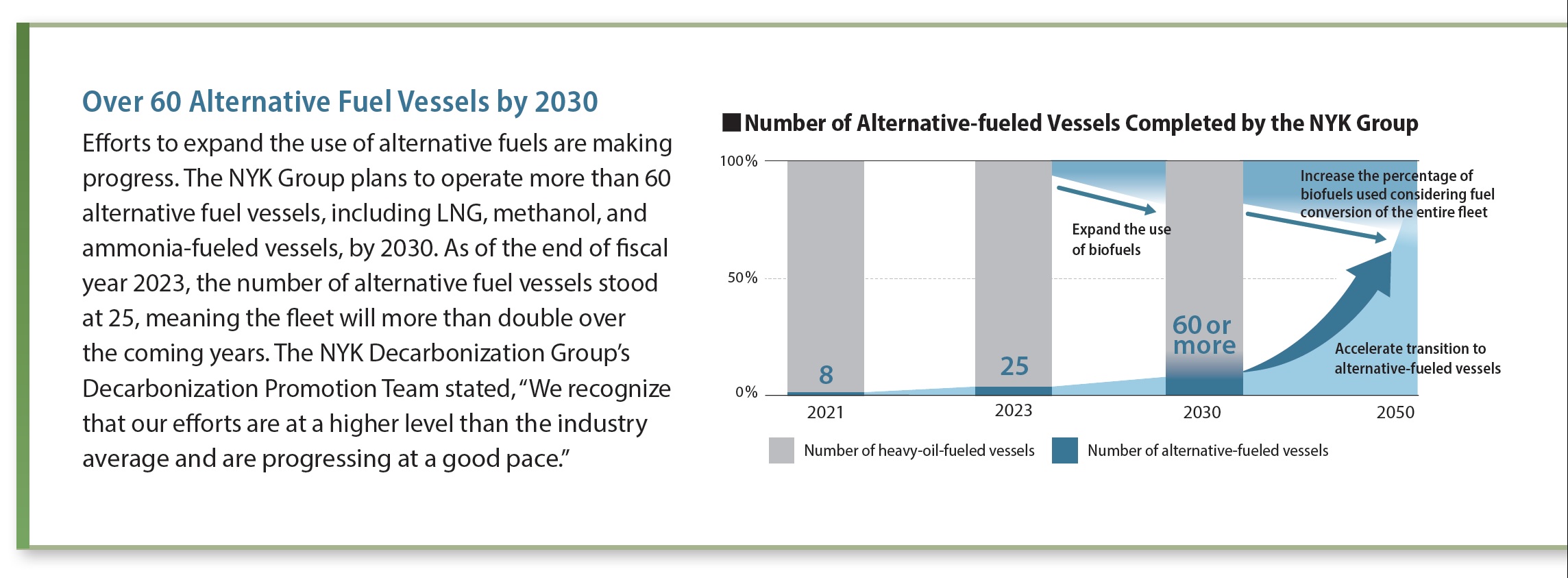
This article was re-edited from the Special Issue of KAIJI PRESS published on March 25, 2025.